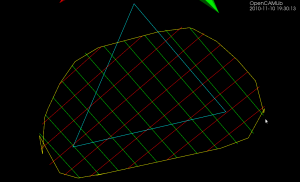
Playing around with the vd-code has highlighted some problems. Using double-precision floating point numbers for coordinates, strange things start to appear when the coordinates are around 1E-6 or so. It's not possible to accurately compute the sign of the in-circle predicate (a 4x4 determinant) and the diagram update should instead be based on topological reasoning.
Category: CAM
Delaunay Triangulation
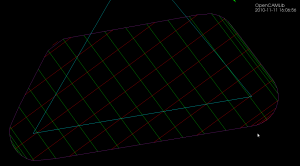
The dual of the Voronoi diagram is the Delaunay triangulation. Here I've modified my earlier VD code to also output the dual (shown in red). If this can be developed further to do constrained Delaunay triangulations (arbitrary pockets with islands) then it will be useful for cutter-location surfaces in opencamlib.
The regular grid is, in the words of the GTS website, "a much more difficult test than it looks".
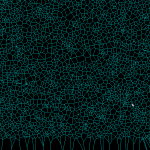
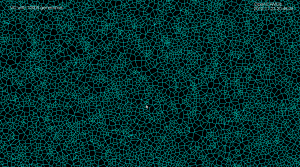
100k sites voronoi diagram
With a bucketing-scheme for nearest-neighbour search in expected time O(1) this voronoi-diagram generation for 100k sites in the [0,1] unit square now runs in 30 s, i.e. it takes about 0.3 ms to insert one point.
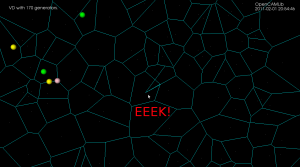
Voronoi diagram algorithm
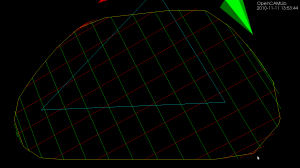
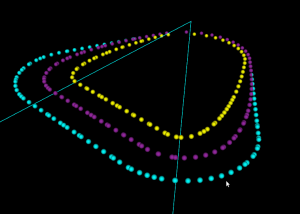
Update: now seems to work for at least 10k generators:
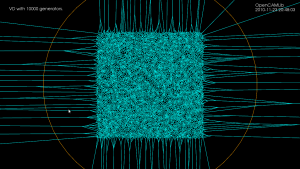
and a zoom-in of the same picture:
One way to compute 2D offsets for toolpath generation is via the voronoi diagram. This video shows the first (somehow) working implementation of my code, which is based on papers by Sugihara and Iri. Their 1992 paper is here: http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/5.163412, then a longer 50-page paper from 1994 here: http://dx.doi.org/10.1142/S0218195994000124, and then there's a more general description of the topology-based approach from 1999 here 10.1007/3-540-46632-0_36, and from 2000 here: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s004530010002
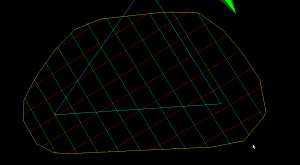
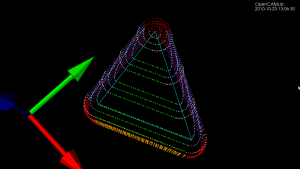
The algorithm works by incrementally constructing the diagram while adding the point-generators one by one. This initial configuration is used at the beginning:
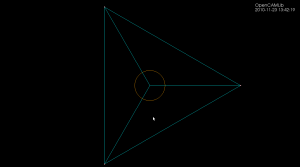
The diagram will be correct if new generator points are placed inside the orange circle (this way we avoid edges that extend to infinity). Once about 500 randomly chosen points are added the diagram looks like this:
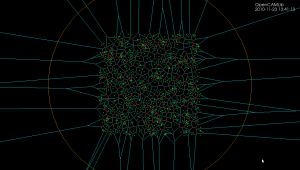
Because of floating-point errors it gets harder to construct the correct diagram when more and more points are added. My code now crashes at slightly more than 500 generators (due to an assert() that fails, not a segfault - yay!). It boils down to calculating the sign of a 4-by-4 determinant, which due to floating-point error goes wrong at some point. That's why the Sugihara-Iri algorithm is based on strictly preserving the correct topology of the diagram, and in fact they show in their papers that their algorithm doesn't crash when a random error is added to the determinant-calculations, and it even works (in some sense) when the determinant calculation is completely replaced by a random number generator. Their 1992 paper constructs the diagram for one million generators using 32-bit float
numbers, while my naive attempt using double here crashes after 535 points... some work to do still then!
CAM toolpaths tend to be based on CAD-geometry in the form of lines, circular arcs, or spline-curves and such. One way forward is to think of a curve as a lot of closely spaced points along the curve. There are also papers which describe how to extend the algorithm for line and arc generators. See the 1996 paper by Imai. There is FORTRAN code for this by Imai over here (I haven't looked at it or tried compiling it...). Held et al. describe voronoi diagram generation for points and lines in 2001: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0925-7721(01)00003-7 and for points, lines, and arcs in 2009 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2008.08.004. This pic from the Held&Huber 2009 paper shows point, line, and arc generators in bold-black, the associated voronoi-diagram as solid lines, and offsets as grey lines.
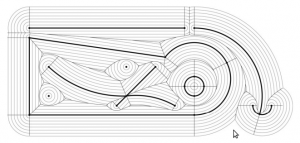
Held has more pictures here: http://www.cosy.sbg.ac.at/~held/projects/pocket_off/pocket.html
Note how within one voronoi-region the offset is determined by the associated generator (a line, point, or arc). It's very easy to figure out the offset within one region: points and arcs have circular offsets, while lines have line offsets. The complete offset path is a result of connecting the offset from one region with the next region.
Better adaptive waterline
Previously the flat() predicate looked only at the number of intervals contained in a fiber when deciding where to insert new fibers in the adaptive waterline algorithm. Here I've borrowed the same flat() function used in adaptive drop-cutter which computes the angle between subsequent line-segments(yellow), and inserts a new fiber(cyan) if the angle exceeds some pre-set threshold.
This works on the larger Tux model also. However, there's no free lunch: the uniformly sampled waterline (yellow) runs in about 2 s (using OpenMP on a dual-core machine), while the adaptively sampled waterline takes around 30s to compute (no OpenMP).
The difference between the adaptive (red) and the uniformly sampled (yellow) waterlines is really only visible when zooming in on sharp corners or other details. Compare this to adaptive drop-cutter.
Waterline problem
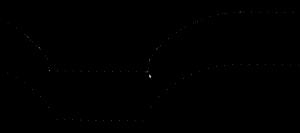
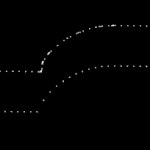
I was trying to work on a new adaptive waterline feature, but ended up uncovering an old existing problem/bug with waterline. I think it has to be a problem in either building the weave from the fibers, or constructing the planar embedding of the weave.
The yellow waterline should obviously be a smooth loop around the outside of the weave (red/green fibers) and not a zigzag journey back and forth... 🙁
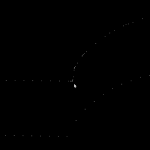
Update: this is better now:
Update2: here's a figure where new fibers (red and green) are inserted adaptively where the shape of the waterline changes most. There's something wrong with building the planar embedding for this weave, so no yellow adaptive waterline path yet...
Update3: some progress at last (fixed a bug in adaptive drop-cutter at the same time):
Adaptive sampling drop-cutter
Inspired by this post on the pycam forum and by this 1993 paper by Luiz Henrique de Figueiredo (or try another version) I did some work with adaptive sampling and drop-cutter today.
The point based CAM approach in drop-cutter, or axial tool-projection, or z-projection machining (whatever you want to call it) is really quite similar to sampling an unknown function. You specify some (x,y) position which you input to the drop-cutter-oracle, which will come back to you with the correct z-coordinate. The tool placed at this (x,y,z) will touch but not gouge the model. Now if we do this at a uniform (x,y) sampling rate we of course face the the usual sampling issues. It's absolutely necessary to sample the signal at a high enough sample-rate not to miss any small details. After that, you can go back and look at all pairs of consecutive points, say (start_cl, stop_cl). You then compute a mid_cl which in the xy-plane lies at the mid-point between start_cl and stop_cl and, call drop-cutter on this new point, and use some "flatness"/collinearity criterion for deciding if mid_cl should be included in the toolpath or not (deFigueiredo lists a few). Now recursively run the same test for (start_cl, mid_cl) and (mid_cl, stop_cl). If there are features in the signal (like 90-degree bends) which will never make the flatness predicate true you have to stop the subdivision/recursion at some maximum sample rate.
Here the lower point-sequence (toolpath) is uniformly sampled every 0.08 units (this might also be called the step-forward, as opposed to the step-over, in machining lingo). The upper curve (offset for clarity) is the new adaptively sampled toolpath. It has the same minimum step-forward of 0.08 (as seen in the flat areas), but new points are inserted whenever the normalized dot-product between mid_cl-start_cl and stop_cl-mid_cl is below some threshold. That should be roughly the same as saying that the toolpath is subdivided whenever there is enough of a bend in it.
The lower figure shows a zoomed view which shows how the algorithm inserts points densely into sharp corners, until the minimum step-forward (here quite arbitrarily set to 0.0008) is reached.
If the minimum step-forward is set low enough (say 1e-5), and the post-processor rounds off to three decimals of precision when producing g-code, then this adaptive sampling could give the illusion of "perfect" or "correct" drop-cutter toolpaths even at vertical walls.
The script for drawing these pics is: http://code.google.com/p/opencamlib/source/browse/trunk/scripts/pathdropcutter_test_2.py
Here is a bigger example where, to exaggerate the issue, the initial sample-rate is very low:
waterline with bullcutter
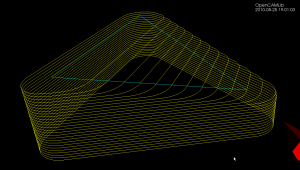
Update: Here is another example with the CL-points coloured differently. At each z-height the innermost loop is with the ball-cutter, next is the bullcutter, and the outermost loop is calculated for a cylindrical cutter. The points are coloured based on which test (vertex, facet, edge) produced them. Vertex-test points are red. Facet-test points are green. The edge-test is further subdivided into (1) a test for horizontal edges (orange), (2) a test for contact with the cylindrical shaft of the cutter (magenta), and (3) the general edge-push function (light blue for ball/bull, pink for cyl). If/when I get the cone-cutter done the cutter-location algorithms in opencamlib should be complete (at least for the moment...), and I can move on to more interesting high-level algorithms.
This figure shows one of the first times I got the push-cutter/waterline algorithm working for bullcutter (filleted endmill, bull-nose cutter, toroidal cutter, a dear child has many names...).
The thin cyan lines are edges of a triangle. The outer cyan spheres are valid cutter locations (CL-points) for a cylindrical endmill. The innermost yellow CL-points are for a spherical (or ball-nose) endmill. Between these two point-sets the new development is the magenta points, which are CL-points for a bull-nose cutter.
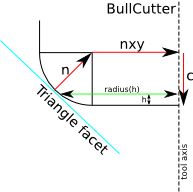
The algorithm works by pushing the cutter at a specified Z-height along either the X-axis or the Y-axis into contact with the triangle. There are three sub-functions for handling the case where the cutter makes contact with a vertex, the triangle facet, and an edge. The edge-contact case is the non-trivial (read "hard") one. The approach I am using is based on the offset-ellipse, courtesy of the freesteel blog. Pushing a toroid into contact with an edge/line is equivalent to pushing the cylindrical "core" of the bullcutter into contact with an edge that has been 'inflated' to a cylinder with a radius equal to the bullcutter corner radius. Slicing this cylinder/tube with a z-plane gives us an ellipse, and the sought cutter-location lies on the offset of this ellipse. I should make some diagrams and post longer/better explanation later (I wonder if anyone reads these 🙂 ).
The bullcutter is important not only in itself, but also because it is the offset of a cylindrical cutter. When we want to do z-terrace roughing with a cylindrical cutter, and specify a stock-to-leave value, we do it by calculating the toolpath with cylcutter->offsetCutter() which is a bullcutter, and then actually machining with the cylindrical cutter. That will achieve the desired stock to leave (to be removed later by a finish operation).
OpenCAMLib from HeeksCNC
I've tried using opencamlib through heekscnc. With a few minor modifications to the ocl_funcs.py script I got it working. Although ocl prints some debug information and a progress bar to the console when run standalone, I couldn't find that window in heekscnc. Even with this small example there are obvious issues with memory management (sometimes 8 Gb wasn't enough!) on either the heekscnc or ocl-side of things (or both!).
On Ubuntu 10.04LTS getting all the bits and pieces, compiling them and installing them was a breeze thanks to this install script. However the GUI feels very "sticky" with the mouse cursor not really going where I want it to go, and the keyboard focus being in surprising places when I want to edit properties. It must be possible to make a GUI that feels good to use with wxgtk, right?
I think currently the inputs and outputs of these two operations, "ZigZag" and "Waterline", are defined in at least three places: ocl itself, the python script ocl_funcs.py, and in the heekscnc c++ GUI code that displays the menus and buttons. Something like introspection or reflection or naked objects would be needed so that a GUI can query the libraries that are present on what operations they offer, what input they need, and what output they produce. If I get my head around some generic-enough GUI ideas I might try writing something myself also. Most probably based on Qt and VTK. In any case the cutting-simulation needs to be driven from a C++ GUI, for performance, I think.
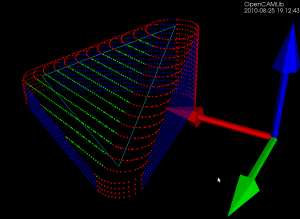
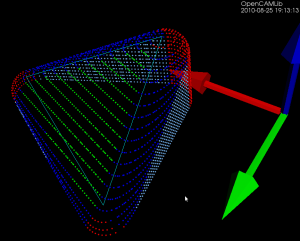
Radial tool projection
The basic operation when producing waterline-paths is to push the cutter along either the X or Y axis (red and green arrows) into contact with a triangle (cyan lines). That's done through three different functions, one each for the vertices, facet, and edges of the triangle. The vertex test (results shown as red dots) and the facet test (green dots) are straightforward to implement. The edge-test (blue dots) is more involved. The above figure is for a CylCutter where the edge-test is implemented through the vertex-test (thus red dots along the edges), but this figure for a BallCutter shows the colors better:
Blue dots show edge-contacts with the spherical part of the cutter, light-blue dots show edge-contacts with the cylindrical shaft of the cutter.
The vertex test requires only a radius(h) function that returns the radius of the cutter at height h. The facet test needs three parameters (n, nxy, c) for each cutter, which define where the cutter should be located relative to a point which lies on the facet. From the CC-point on the facet we go a distance n along the 3D unit-normal, then a distance nxy along a unit-normal in the XY-plane to find the cutter center. From the cutter center we go down along the z-axis by a distance c to find the CL-point.
Figuring out the (n,nxy,c) parameters for CylCutter and BallCutter is left as an exercise for the reader.
These points are then hooked up in the correct order to produce waterlines like this (CylCutter on the left, BallCutter on the right).
The edge-test for CylCutter reduces to a 2D problem of line-line intersections, while the edge-test for BallCutter can be done by intersecting a cylinder/tube around the edge with a line. The filleted/toroidal/BullCutter edge-test is much harder. Here I've just implemented the special case where the edge is horizontal and the solution is easy to find analytically. The general case where the edge slopes up or down requires an iterative solution to either a quartic or the offset-ellipse problem.